Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction
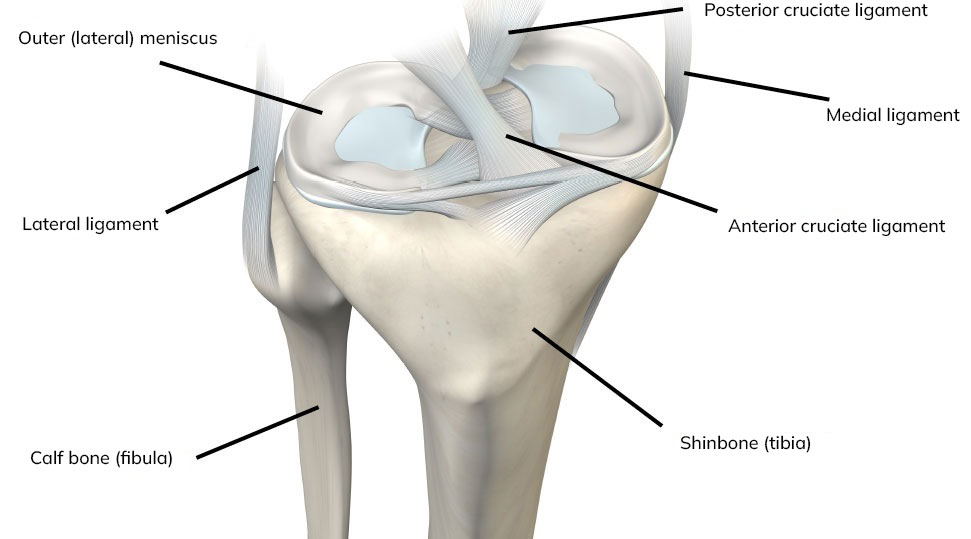
What is a torn anterior cruciate ligament (ACL)?
What are the symptoms?
If you tear your anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), it may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- A popping sensation in the knee during the twisting injury
- Pain and inability to participate in sports activities
- Immediate swelling of the knee
- Difficulty in bending and straightening the knee
- Instability.
How do we diagnose it?
The diagnosis is made in the examination room during the physical examination. Additional tests are always conducted:
- An X-ray: This allows us to quickly assess whether there is a fracture or any signs of degeneration
- An MRI scan: This allows us to study all the structures in the knee and determine the extent of the damage.
What does the treatment consist of if you have torn your anterior cruciate ligament (ACL)?
When the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is torn, swelling of the knee occurs and it becomes difficult to fully extend and flex the knee. Therefore, the early treatment approach involves taking anti-inflammatory medication to reduce the swelling. It is also recommended to start with physiotherapy to normalize the knee’s range of motion. In a small group of patients, the knee may recover well without the need for surgery. However, for most athletes and patients, instability will persist. That is why a reconstruction of the anterior cruciate ligament is performed.
Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) reconstruction
The surgery
The surgery takes place as a day procedure, and you are usually allowed to go home the same day. The operation can be performed under general anesthesia or with a spinal anesthesia, depending on your preference. Often, a local anesthetic is also given in the groin area, known as a femoral block, to minimize pain during the first 48 hours after the surgery.
During the operation, the following steps are carried out:
- First, the tissue (hamstring tendons, quadriceps tendon, or patellar tendon) is harvested to create the new cruciate ligament.
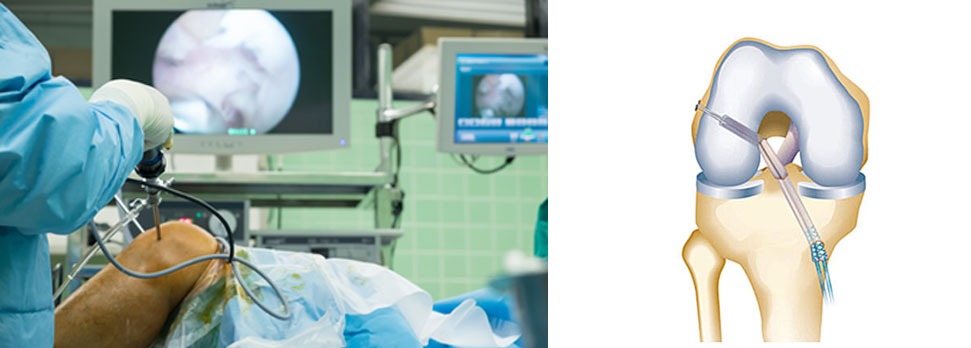
- A knee arthroscopy is performed to inspect the entire knee. If there is any meniscus or cartilage damage, it can be treated.
- The remnants of the old anterior cruciate ligament are removed, and tunnels are drilled in the thigh bone (femur) and shinbone (tibia).
- The newly harvested tissue is placed in the tunnels and secured as the new cruciate ligament.
- The instruments are removed, and the skin is closed with absorbable sutures.